The super-fast “Hyperloop” travel concept is just the latest in a series of big, bold dreams by billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk.
Musk unveiled his proposed Hyperloop transportation system Monday (Aug. 12), claiming that it could blast passenger-packed pods through long tubes at about 760 mph (1,220 km/h) using energy derived from the sun.
The Hyperloop is potentially revolutionary, making it a typical Musk idea. Here’s a look at six ways the South African-born billionaire is changing the world — or is hoping to in the future.
Pioneering e-commerce
Elon co-founded the online financial services company X.com in 1999. In 2000, X.com merged with Confinity, which had developed an online payment system called PayPal. Though the combined firm at first retained the X.com moniker, it changed its name to PayPal in early 2001.
PayPal, which has helped make Internet payments and money transfers routine, grew quickly and dramatically. It was acquired by eBay in October 2002.
Private spaceflight
Musk founded the private spaceflight firm SpaceX in 2002 and currently serves as its CEO and chief designer.
SpaceX has already made history, becoming the first private company to deliver a spacecraft to the International Space Station. SpaceX’s unmanned Dragon capsule first visited the orbiting lab on a demonstration mission in May 2012 and has completed two bona fide cargo runs since. The company holds a $1.6 billion contract with NASA to make 12 such flights with Dragon and its Falcon 9 rocket.
SpaceX is also developing a crewed version of Dragon, and Musk hopes to score another NASA deal to fly astronauts to the space station. The firm is also working on a prototype reusable rocket called Grasshopper, in the hopes of making spaceflight far cheaper and more efficient.
Musk has said repeatedly that he founded SpaceX primarily to help humanity become a multiplanet species.
Making electric cars cool
Musk has a long-held interest in electric-vehicle technology, and in 2003, he co-founded Tesla Motors, which manufactures electric cars and the battery packs that power them.
Tesla is helping many people view electric cars in a new light. For example, the company’s Model S sedan was named 2013 Car of the Year by both Motor Trend and Automobile Magazine. One version of the Model S can go from 0 to 60 mph (96 km/h) in 4.0 seconds, according to Motor Trend.
The company is expanding rapidly. In May, officials announced that Tesla had already paid off the entire loan it received from the U.S. Department of Energy in 2010, nine years ahead of schedule. The firm also notched profits in the first and second quarters of 2013.
Renewable energy
Musk’s interest in electric cars stems in part from his concern about the effects of climate change, so it makes sense that he’s involved with a big renewable-energy venture.
Musk serves as chairman of SolarCity, which designs and installs clean-energy systems for households, businesses, universities and other organizations. The firm, which was founded in 2006, has thousands of customers across 14 states, according to its website.
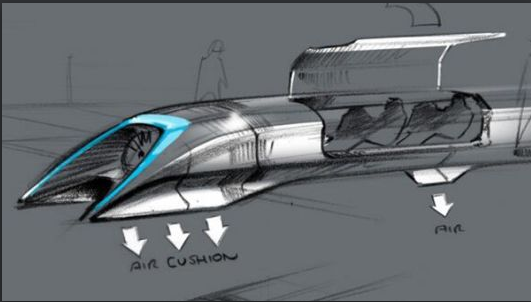
The Hyperloop
Musk explained Monday, would use electric motors to accelerate 6.5-foot-wide (2 meters) pods to nearly supersonic speeds. These pods would zoom through long tubes, which would be mounted on pylons to minimize construction costs, reduce earthquake risk and ease right-of-way issues.
Musk sees the system as a cheaper, faster alternative to California’s proposed $70 billion high-speed rail system, estimating that a Hyperloop line could be built from Los Angeles to San Francisco for $6 billion or so. (A trip between the two cities would take just 30 minutes, Musk said.)
The entrepreneur hopes other innovators will improve upon the Hyperloop design and run with it, since he’s busy developing Tesla and SpaceX. But Musk said he’s interested in building a demonstration model to help get the Hyperloop off the ground.
“I’d like to see something like this happen,” Musk told reporters during a conference call Monday. “I don’t really care much one way or the other if I have any economic outcome here. But it would be cool to see a new form of transport happen.”